6 Hacks for Guaranteed Project Risk Management Success Now
Share it
Introduction
Project risk management is the key to delivering successful projects in 2024 and beyond.
By proactively identifying, assessing, and controlling potential threats, you can minimize their impact and keep your projects on track.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the six essential hacks for effective project risk management:
- Identify potential risks early
- Assess and prioritize risks
- Develop a risk response plan
- Implement risk response strategies
- Monitor and control risks throughout the project
- Conduct post-project risk analysis
Whether you’re a seasoned project manager or just starting, mastering these fundamentals will help you confidently navigate the complexities of modern projects.
So, let’s explore how you can harness the power of project risk management to drive success in 2024.
Step 1: Identify Potential Risks Early
Identifying potential risks early in the project lifecycle is crucial for effective risk management.
Begin by brainstorming with your project team to uncover possible risks impacting the project’s success.
Encourage open communication and create a safe environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their concerns and insights.
Categorize the identified risks into specific project areas, such as budget, timeline, resources, or scope.
This categorization helps to organize risks and ensures that no area is overlooked.
Document all identified risks in a risk register, a central repository for risk-related information throughout the project.
Techniques for Risk Identification
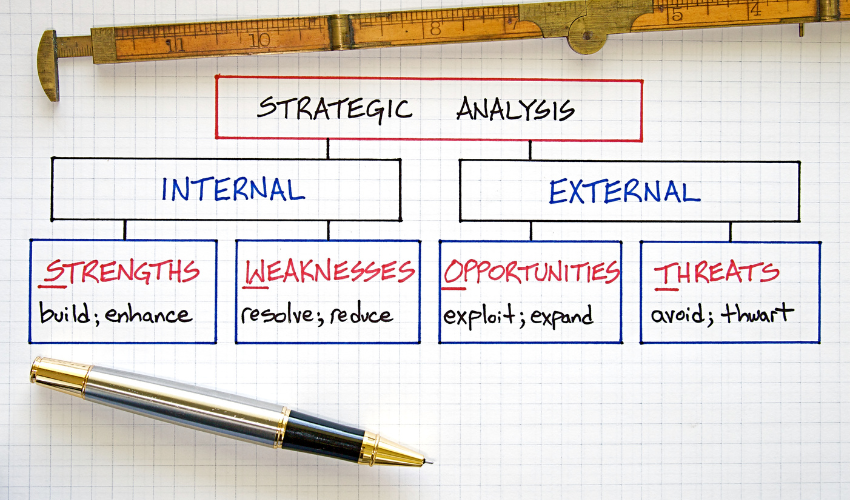
- SWOT analysis: Assess the project’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
- Expert interviews: Consult with subject matter experts to gain insights into potential risks
- Checklist analysis: Use historical data and industry best practices to create risk checklists
Step 2: Assess and Prioritize Risks
Once potential risks have been identified, evaluate the likelihood and impact of each risk.
Assign risk scores based on the probability of the risk occurring and the severity of its potential consequences.
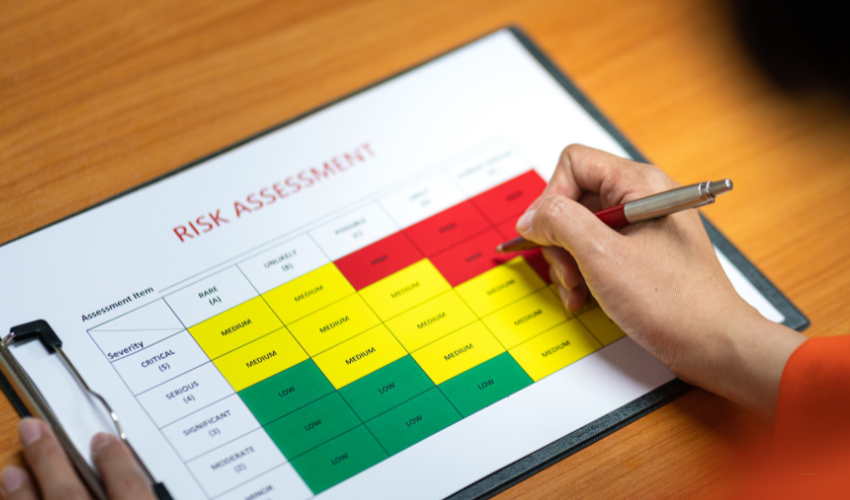
Use a risk matrix to visualize the relationship between probability and impact, helping to prioritize risks based on their overall risk level.
Prioritize risks based on their potential effect on project success.
High-priority risks, those with a high probability and significant impact, should receive the most attention and resources.
Medium and low-priority risks should also be addressed with effort proportionate to their potential impact.
Risk Assessment Tools
- Probability and impact matrix: Plot risks on a grid based on their likelihood and potential consequences
- Risk rating scales: Assign numerical values to risks based on predefined criteria
- Monte Carlo simulation: Model the potential outcomes of risks using statistical analysis
Step 3: Develop a Risk Response Plan
With risks identified and prioritized, develop a comprehensive risk response plan.
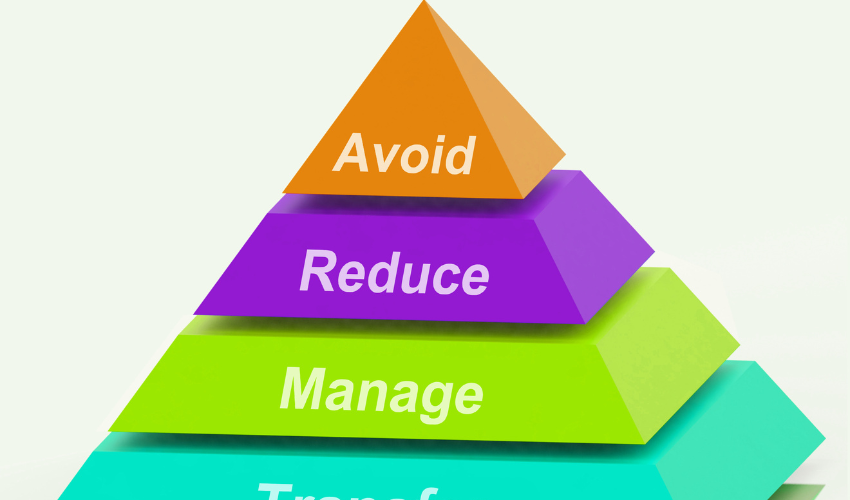
Based on each risk’s priority level and the project’s risk tolerance, determine strategies to mitigate, avoid, transfer, or accept it.
Assign risk owners responsible for implementing and monitoring the response plans for their assigned risks.
Establish contingency plans for high-priority risks. These plans outline the steps to be taken if the risk occurs, minimizing its impact on the project.
Allocate contingency reserves, both budgetary and time-based, to account for risks’ potential impact.
Risk Response Strategies
- Risk mitigation: Take proactive steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk
- Risk avoidance: Alter the project plan to eliminate the risk entirely
- Risk transfer: Shift the risk’s impact to a third party, such as through insurance or contracts
- Risk acceptance: Acknowledge the risk and plan to manage its consequences if it occurs
Step 4: Implement Risk Response Strategies
With the risk response plan in place, it’s time to execute the planned risk response actions.
Allocate resources and budget for risk management activities, ensuring risk owners have the necessary support to implement their assigned strategies.
Communicate the risk response plans to all relevant stakeholders, including project team members, sponsors, and clients.
Clear communication ensures that everyone is aware of the potential risks and the steps being taken to address them.
Implementing Risk Response
- Assign responsibilities: Clearly define roles and responsibilities for risk response implementation.
- Provide resources: Allocate necessary personnel, budget, and tools.
- Monitor progress: Regularly review the implementation of risk response strategies.
Step 5: Monitor and Control Risks Throughout the Project
Risk management is an ongoing process that continues throughout the project lifecycle.
Regularly review and update the risk register to reflect changes in the project environment and the effectiveness of risk response strategies.
Track the effectiveness of risk response strategies using predefined metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs).
This data helps to identify areas where risk management efforts may need to be adjusted.
As the project progresses, continue to identify and assess new emerging risks.
Regularly engage with the project team and stakeholders to uncover potential risks and address them proactively.
Risk Monitoring Techniques
- Risk audits: Conduct periodic reviews of the risk management process and its effectiveness
- Risk metrics: Track predefined risk management KPIs to measure success
- Risk status reports: Provide regular updates on the status of risks and response strategies
Step 6: Conduct Post-Project Risk Analysis
At the project’s conclusion, evaluate the overall effectiveness of the risk management efforts.
Assess how well risks were identified, assessed, and responded to throughout the project lifecycle.
Document lessons learned from the risk management process, including successes, challenges, and areas for improvement.
These insights can be valuable for future projects, helping to refine and optimize the organization’s risk management approach.
Based on the post-project analysis, update the organization’s risk management processes and templates.
Incorporate best practices and lessons learned to improve risk management capabilities continuously.
Post-Project Risk Review
- Conduct a risk management audit: Evaluate the effectiveness of the risk management process.
- Solicit feedback: Gather input from project team members and stakeholders on the risk management approach.
- Update risk management assets: Refine risk management templates, tools, and processes based on lessons learned.
By following these six essential steps, project managers can effectively identify, assess, and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle.
A proactive and comprehensive approach to risk management helps minimize potential issues’ impact and increases the likelihood of project success.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Project Risk Identification
TL;DR:
- Brainstorming sessions, risk breakdown structures, and expert judgment help identify project risks
- SWOT analysis and checklists provide structured approaches to risk identification
- Involving diverse stakeholders is key to uncovering a wide range of potential risks
Brainstorming Sessions
Brainstorming sessions are a powerful tool for identifying project risks.
By bringing together a diverse group of project stakeholders, you can tap into a wealth of knowledge and experience to uncover potential issues that may not be apparent to anyone.
To maximize brainstorming sessions, it’s important to create a structured environment that encourages open discussion.
This can be achieved by setting clear goals for the session, establishing ground rules for participation, and using facilitation techniques to keep the conversation on track.
Benefits of Brainstorming Sessions
- Leverage collective knowledge and experience of project team and stakeholders
- Encourage creative thinking and problem-solving
- Build a shared understanding of project risks among team members
Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS)
A risk breakdown structure (RBS) is a hierarchical representation of potential risk categories within a project.
By creating an RBS, project managers can ensure that they take a comprehensive risk identification approach.
The RBS serves as a checklist of sorts, helping project teams consider all possible risk sources systematically.
Each level of the hierarchy represents a different risk category, with more specific risks identified at lower levels.
Creating an Effective RBS
- Start with high-level risk categories, such as technical, financial, or organizational risks.
- Break down each category into more specific sub-categories
- Continue to drill down until all potential risks have been identified
- Use the RBS as a guide during brainstorming sessions and other risk-identification activities
Expert Judgment
Expert judgment is another valuable tool for identifying project risks.
By consulting with subject matter experts who have deep knowledge of the industry, technology, or methodology involved in the project, project managers can gain insights into potential issues that may not be obvious to the project team.
In addition to industry experts, experienced project managers can provide valuable input on potential risks based on their past experiences with similar projects.
By leveraging this expertise, project teams can anticipate and mitigate risks more effectively.
Leveraging Expert Judgment Effectively
- Identify relevant subject matter experts early in the project planning process
- Schedule structured interviews or workshops to gather input from experts
- Use targeted questions to elicit insights on potential risks and mitigation strategies
- Document expert input and incorporate it into the project’s risk management plan
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that can be adapted for project risk identification.
Project teams can uncover a wide range of potential risks by examining the project’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT).
Strengths and opportunities represent positive factors that can help the project succeed, while weaknesses and threats represent potential risks that could derail the project.
By systematically considering these factors, project teams can develop a more complete picture of the risks facing their project.
Conducting a SWOT Analysis for Risk Identification
- Assemble a diverse group of project stakeholders
- Brainstorm the project’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
- Consider both internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) and external factors (opportunities and threats)
- Prioritize the identified risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence
Checklists
Checklists are a simple but effective tool for ensuring all potential risks are considered.
By creating a standardized list of risk categories and specific risks, project teams can systematically review each item to determine whether it applies to their project.
Checklists can be developed based on the organization’s past experience with similar projects, industry best practices, or input from subject matter experts.
They can be used with other risk identification techniques, such as brainstorming sessions or SWOT analysis, to ensure no potential risks are overlooked.
Developing and Using Risk Identification Checklists
- Create a comprehensive list of risk categories and specific risks
- Customize the checklist to the specific needs of the project
- Review the checklist with the project team and stakeholders to gather input
- Use the checklist as a guide during risk identification activities
- Update the checklist regularly based on new information or changes to the project
Project managers can use a combination of these tools and techniques to identify potential risks thoroughly and systematically.
The key is to involve a diverse group of stakeholders, leverage expert knowledge, and use structured methods to ensure that all possible risks are uncovered and documented.
With a comprehensive understanding of the project’s risks, teams can then proceed to assess and prioritize those risks in the next phase of the risk management process.
Quantitative and Qualitative Risk Assessment Methods
- Prioritize risks effectively using quantitative and qualitative assessment techniques
- Make data-driven decisions to mitigate potential project roadblocks
- Communicate risk assessment findings to stakeholders for better alignment
Probability-Impact Matrix
A probability-impact matrix is a powerful tool for visualizing and prioritizing project risks.
Project managers can quickly identify which risks require the most attention by plotting risks on a matrix based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact.
To create a probability-impact matrix, start by assigning each risk a probability score (e.g., 1-5) and an impact score (e.g., 1-5).
Then, plot the risks on a grid with probability on one axis and impact on the other.
Risks that fall in the high-probability, high-impact quadrant should be prioritized for mitigation.
Benefits of Using a Probability-Impact Matrix
- Provides a clear visual representation of project risks
- Helps prioritize risk mitigation efforts
- Facilitates communication with stakeholders about risk priorities
Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation is a quantitative risk assessment technique that uses statistical modeling to estimate the probability of different project outcomes.
By running multiple simulations with various risk scenarios, project managers can identify the most likely project completion date and budget based on the identified risk factors.
To perform a Monte Carlo simulation, follow these steps:
- Define the project schedule and budget
- Identify key risk variables and their probability distributions
- Run multiple simulations using a Monte Carlo software tool
- Analyze the results to determine the most likely outcomes and risk impacts
Advantages of Monte Carlo Simulation
- Provides a range of possible outcomes rather than a single point estimate
- Incorporates the effects of multiple interrelated risks
- Helps determine contingency budgets and schedules based on risk levels
Decision Tree Analysis
Decision tree analysis is a qualitative risk assessment method that maps out risk scenarios and their potential consequences.
Project managers can evaluate the costs and benefits of various risk response strategies by creating a visual representation of the possible outcomes.
To create a decision tree, identify the key decision points and the possible outcomes at each point.
Assign probabilities and costs/benefits to each outcome, and then calculate the expected value of each decision path.
Based on the risk assessment, this helps determine the most advantageous course of action.
Benefits of Decision Tree Analysis
- Provides a structured approach to decision-making under uncertainty
- Helps compare the costs and benefits of different risk response strategies
- Facilitates communication with stakeholders about the reasoning behind risk-related decisions
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is a quantitative risk assessment technique that examines how changes in key project variables affect the overall project outcomes.
By identifying which variables impact the project most, managers can prioritize their risk mitigation efforts.
To perform a sensitivity analysis, follow these steps:
- Identify the key project variables (e.g., cost, duration, resources)
- Define the range of possible values for each variable
- Calculate the project outcomes for each combination of variable values
- Analyze the results to determine which variables have the greatest impact
Advantages of Sensitivity Analysis
- Identifies the most critical project variables for risk management
- Helps allocate risk management resources effectively
- Provides insights into the robustness of the project plan
Expert Judgment
Expert judgment is a qualitative risk assessment method that relies on the knowledge and experience of subject matter experts to identify and evaluate project risks.
By leveraging the insights of experts, project managers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the potential risks and their impacts.
To incorporate expert judgment into the risk assessment process, consider the following:
- Identify relevant subject matter experts
- Conduct structured interviews or workshops to elicit risk insights
- Document and prioritize the identified risks based on expert input
- Regularly review and update the risk assessment with expert feedback
Benefits of Expert Judgment
- Provides valuable insights from experienced professionals
- Helps identify risks that may be overlooked by other assessment methods
- Facilitates buy-in and support from key stakeholders
Conclusion
Risk assessment is a crucial component of project management, and using a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods can provide a comprehensive understanding of project risks.
By applying these methods, project managers can make informed decisions to mitigate risks and ensure project success.
Effective Risk Communication and Reporting
- Ensure stakeholders are informed and engaged in risk management
- Establish clear communication channels and reporting formats
- Regularly review and update risk documentation for accuracy and relevance
Risk Management Plan
A well-crafted Risk Management Plan is the foundation for effective risk communication and reporting.
This document should outline the project’s overall approach to risk management, including roles, responsibilities, and communication protocols for risk-related activities.
Key components of a Risk Management Plan include:
Risk Management Objectives
Clearly define the project’s risk management goals and objectives, aligned with the overall project objectives. This helps ensure all risk management activities focus on achieving the desired outcomes.
Risk Management Processes
Detail the specific processes and methodologies for identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and responding to risks. This may include techniques such as brainstorming sessions, SWOT analysis, or Monte Carlo simulations.
Roles and Responsibilities
Assign project team members and stakeholders specific roles and responsibilities for risk management activities. This ensures that everyone understands their part in managing risks and fosters a culture of shared responsibility.
Risk Register
A Risk Register is a centralized repository for capturing and tracking identified risks throughout the project lifecycle.
It is a living document regularly updated as new risks emerge or existing risks evolve.
The Risk Register should include the following information for each identified risk:
- Risk description and category
- Probability and impact assessment
- Risk owner and response strategy
- Status and progress updates
By maintaining a comprehensive Risk Register, project teams can ensure that risks are consistently documented, assessed, and monitored, enabling effective communication and reporting to stakeholders.
Risk Status Reports
Regular risk status reports are essential for keeping stakeholders informed about the project’s risk landscape and the effectiveness of risk response strategies.
These reports should be tailored to the needs and preferences of different stakeholder groups, such as executive sponsors, project team members, or external partners.
Key elements of effective risk status reports include:
Risk Overview
Provide a high-level summary of the project’s risk profile, highlighting any significant changes since the last reporting period. This may include the total number of identified risks, the distribution of risks across categories, or the overall risk exposure.
Key Risks and Response Strategies
Focus on the project’s most critical or high-priority risks, briefly describing each risk and its potential impact. Detail the planned or ongoing response strategies for these risks, including any progress or challenges encountered.
Risk Trends and Lessons Learned
Analyze risk trends over time, identifying any patterns or recurring issues that may require additional attention or resources.
Share lessons learned from successful risk response strategies or challenges faced, helping to improve the project’s risk management approach continuously.
By implementing a robust Risk Management Plan, maintaining a comprehensive Risk Register, and providing regular risk status reports, project teams can ensure effective risk communication and reporting throughout the project lifecycle.
This enables informed decision-making, proactive risk management, and a higher likelihood of project success.
What is Project Risk Management?
TL;DR:
- Project risk management helps identify, assess, and control risks
- Proactive risk management increases project success and stakeholder confidence
- Risk management should be integrated into all project management processes
Definition and Importance
Project risk management identifies, assesses, and controls risks that may affect a project’s objectives.
It involves a systematic approach to managing uncertainty and minimizing the impact of potential threats while maximizing opportunities.
Effective risk management is critical to the success of any project, as it helps project managers and teams anticipate and mitigate potential issues before they occur.
The importance of project risk management cannot be overstated.
By proactively identifying and addressing risks, project teams can increase the likelihood of project success, avoid costly delays, and ensure that project objectives are met within the defined scope, budget, and timeline.
Risk management also helps project managers make informed decisions based on a thorough understanding of potential risks and their impacts.
Benefits of Proactive Risk Management
Proactive risk management offers several key benefits to project teams and organizations:
- Increased likelihood of project success: By anticipating and mitigating potential issues, project teams can minimize the impact of risks on project objectives, leading to a higher probability of project success.
- Better informed decision-making: With a thorough understanding of project risks, managers can make more informed decisions regarding resource allocation, timeline adjustments, and scope changes.
- Enhanced stakeholder confidence: Demonstrating a proactive approach to risk management can boost stakeholder confidence in the project team’s ability to deliver results, even in the face of uncertainty.
Case Study: The Airbus A380 Program
The Airbus A380 program is an excellent example of the importance of proactive risk management.
Despite the project’s complexity and scale, the Airbus team successfully identified and mitigated potential risks, such as supply chain disruptions and technical challenges.
By implementing a robust risk management process, the team delivered the world’s largest passenger aircraft on time and within budget, earning the confidence of stakeholders and customers alike.
Integration with Project Management Processes
To be truly effective, risk management should be an integral part of the overall project management approach.
This means that risks should be considered and addressed throughout all project lifecycle phases, from planning and execution to monitoring and closing.
Integrating risk management into project management processes allows teams to:
- Identify risks early in the project lifecycle, when they are easier and less costly to address
- Continuously monitor and update risk assessments as the project progresses and new information becomes available
- Ensure that risk management activities are aligned with project objectives and stakeholder expectations
Risk Management in Agile Projects
Agile project management methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, present unique challenges and opportunities for risk management.
In Agile projects, risk management is often embedded within the iterative development process. Risks are identified, assessed, and addressed during each sprint or iteration.
To effectively manage risks in Agile projects, teams should:
- Incorporate risk management activities into sprint planning and retrospectives
- Encourage open communication and collaboration among team members to identify and mitigate risks
- Use Agile artifacts, such as the product backlog and burn-down charts, to track and visualize risks and their impacts
Further Reading and Resources
For those looking to delve deeper into the world of project risk management, here are some recommended resources:
- “Project Risk Management: A Practical Implementation Approach” by Michael M. Bissonette – This book provides a comprehensive guide to implementing risk management processes in projects of all sizes and industries.
- “Identifying and Managing Project Risk: Essential Tools for Failure-Proofing Your Project” by Tom Kendrick – This book offers a step-by-step approach to identifying, assessing, and managing project risks, with practical tools and techniques for success.
- The Project Management Institute (PMI) – PMI is a leading professional association for project managers, offering a wealth of resources, certifications, and training programs related to project risk management.
By understanding the fundamentals of project risk management and integrating risk management processes into their projects, teams can increase their chances of success and deliver value to their organizations and stakeholders.
What is Project Risk Management?
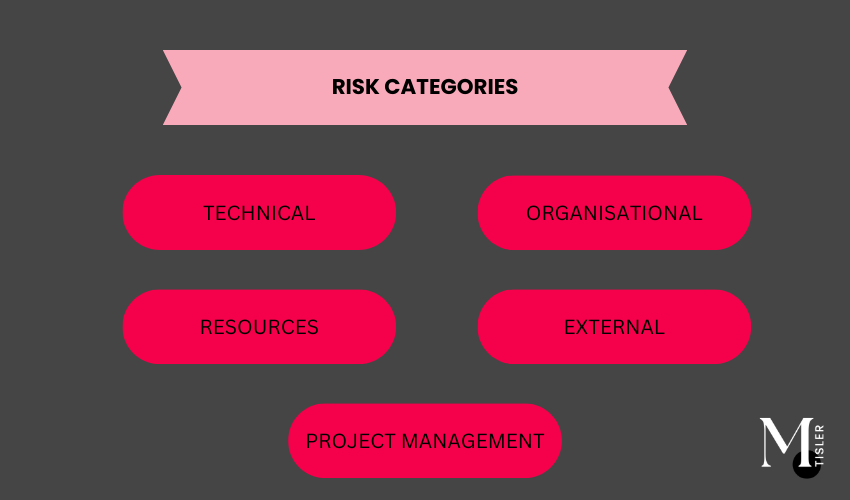
- Identifying and categorizing risks is essential for effective project risk management.
- Common risk categories include technical, organizational, external, project management, and resource risks.
- Understanding these risk categories helps project managers develop targeted mitigation strategies.
Technical Risks
Technical risks are related to the project’s technical requirements, design, or implementation.
These risks can arise from using new technologies, complex integrations, or unproven methodologies. Examples of technical risks include:
- Compatibility issues between different software systems
- Performance limitations of hardware or network infrastructure
- Inadequate testing or quality assurance processes
To mitigate technical risks, project managers should work closely with the technical team to identify potential issues early in the project lifecycle.
Conducting thorough feasibility studies, proof-of-concept tests, and pilot projects can help uncover technical challenges before they become critical risks.
Managing Technical Debt
One key aspect of managing technical risks is addressing technical debt.
Technical debt refers to the long-term costs incurred by taking shortcuts or using suboptimal solutions in software development.
While these shortcuts may save time in the short term, they can lead to increased complexity, reduced performance, and higher maintenance costs over time.
To manage technical debt effectively, project managers should:
- Encourage developers to follow best practices and coding standards
- Allocate time for regular code reviews and refactoring
- Prioritize technical debt reduction in the project backlog
Organizational Risks
Organizational risks arise from the project’s stakeholders, governance structures, or organizational culture.
These risks can impact the project’s success by creating communication barriers, conflicting priorities, or resistance to change. Examples of organizational risks include:
- Unclear roles and responsibilities among project team members
- Lack of executive support or stakeholder buy-in
- Organizational silos or lack of cross-functional collaboration
To mitigate organizational risks, project managers should build strong relationships with key stakeholders and establish clear communication channels.
Conducting stakeholder analysis and developing a comprehensive communication plan can help align expectations and ensure all parties work towards common goals.
Addressing Change Resistance
One common organizational risk is resistance to change. When projects introduce new processes, technologies, or ways of working, some stakeholders may hesitate to adopt these changes.
To address change resistance, project managers can:
- Involve stakeholders in the planning process to foster a sense of ownership
- Communicate the benefits of the change and how it aligns with organizational goals
- Provide training and support to help stakeholders adapt to new processes or tools
External Risks
External risks originate from factors outside the project team’s control.
These risks can be challenging to predict and mitigate, often involving external stakeholders, market conditions, or regulatory requirements.
Examples of external risks include:
- Changes in regulatory requirements or industry standards
- Shifts in market demand or customer preferences
- Issues with suppliers or third-party vendors
Project managers should stay informed about industry trends and regulatory changes to manage external risks.
Conducting regular environmental scans and engaging with external stakeholders can help identify potential risks early on.
Developing contingency plans and building flexibility into the project schedule can also help mitigate the impact of external risks.
Supplier Risk Management
One critical aspect of managing external risks is supplier risk management.
Projects often rely on external suppliers for materials, components, or services.
If these suppliers fail to deliver on time, within budget, or to the required quality standards, it can significantly impact the project’s success.
To mitigate supplier risks, project managers should:
- Conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers
- Establish clear performance metrics and service level agreements (SLAs)
- Monitor supplier performance regularly and address issues promptly
Embracing Risk Management: Your Path to Project Success
Project risk management is not just a box to check off—it’s a vital practice that can make or break your project’s success.
By identifying, assessing, and controlling risks, you’re proactively protecting your project from potential pitfalls.
Implementing the six key steps outlined in this article will help you establish a robust risk management framework.
From early risk identification to post-project analysis, each step minimizes threats and maximizes opportunities.
However, effective risk management goes beyond just following a process. It requires a shift in mindset that embraces risk as an inevitable part of any project.
By fostering a culture of open communication and continuous improvement, you can confidently empower your team to anticipate and respond to risks.
So, what’s your next move?
Start by reviewing your current risk management practices and identifying areas for improvement.
Engage your team in the process, and make risk management a regular topic of discussion in your project meetings.
Remember, the most successful projects don’t just react to risks, but actively seek them out and address them head-on.
Are you ready to take your risk management game to the next level?
Related Articles
- link
- link
- link

Hi, I’m Myriam.
I love blending tech with change management, user experience, project management, business analysis, streamlining processes, improving customer journeys, and designing business structures. While I’m not the top expert, I enjoy exploring these areas and sharing my insights. Whether it’s for large corporations or small startups, I’m passionate about finding efficient ways for them to work. I enjoy experimenting with new recipes and attending artsy events when I’m not doing that. This blog is my space to chat about all the cool business and tech topics I have discovered.